TABLE OF CONTENTS
Most times, we reach for over-the-counter products to help with our skincare needs. However, while products are available to assist with most, if not all our skincare needs, research most times contents that food, what we put into our body, does impact the skin, which is its largest and primary protective organ. In fact, it covers the entire external surface and is the first point of physical barrier against the environment (Lopez-Ojeda et. al. 2022). As such, taking care of it should be paramount to our wellness routine.
While topical products may offer immediate relief or enhanced results over time, foods are essential for the long term and the overall look and feel of the skin. Further, I am also an advocate for a balanced diet, but it certainly doesn’t hurt to know, off hand, some of the foods that can greatly help with the skin and its overall health. Let’s discuss!
You can read more on the skin in this post.
The Discussion
Beauty starts from within which is both a famous saying and a very effective mantra. As such, seeing that the skin is the body’s largest organ, what better way to take care of it and keep it healthy and youthful, even as we age, than through our diet? Research contends that the skin reflects the overall inner-health status, especially as we age (Schagen et al., 2012). Interestingly, the study of how foods can impact the skin has always been a topic of intrigue by researchers as well as physicians over the years (Schagen et al., 2012).
Additionally, vitamins, minerals, carotenoids, tocopherols and flavonoids possess protective components including antioxidants which have been widely used in the skincare industry for topical treatment. They are also used in the form of supplements either to maintain youthful skin, treat particular conditions or just help with the overall appearance of the skin (Schagen et al., 2012).
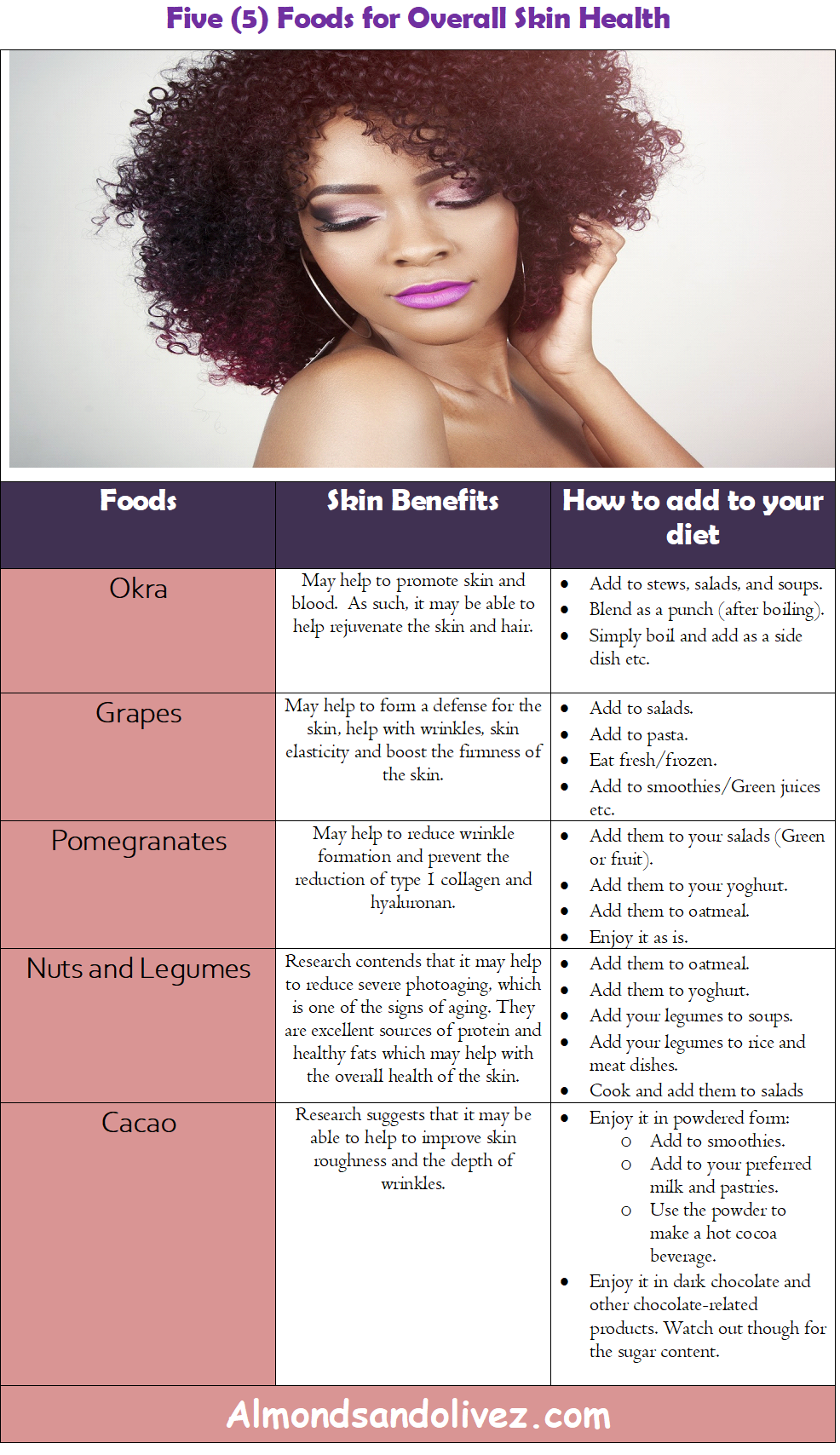
In this article, we will be exploring five (5) foods that research has shown may be able to enhance the skin, from the inside out. These include okra, grapes, pomegranates, nuts and legumes and cocoa. The article will also provide useful links to another detailed post on the skin and ingredients that can help to maintain its health, both in the short and long term.
You can read more on the skin in this post.
Five (5) Foods for Healthy and Beautiful Skin:
- Okra
- Grapes
- Pomegranates
- Nuts and Legumes
- Cocoa
Okra and the Skin
Okra or okro (Abelmoschus esculentus) is a vegetable crop that grows mostly in the tropical and sub-tropical regions of the world (Gemede et al. 2015). Almost all parts of the okra are edible from its fresh leaves including its seeds (Gemede et al. 2015). However, it is the immature fruits which are often consumed as a vegetable and can be used in soups, stews, salads, or any other dish as per your liking. After cooking, it becomes of a mucilaginous consistency. This is where most of its medicinal value lies (Gemede et al. 2015).
Research contends that its mucilage can be used as a plasma replacement or to expand blood volume (Gemede et al. 2015). As such, research purports that okra can be used to promote healthy skin and blood (Bakre and Jaiyeoba, 2009). This is because one hundred (100) grams of okra comprises about twenty-seven (27%) percent of the recommended dietary intake (RDI) of vitamin C and fifty (50%) RDI of vitamin K. Both these vitamins are essential to health as Vitamin C is a potent antioxidant that helps with the growth and repair of bodily tissues (Bakre and Jaiyeoba, 2009) while vitamin K plays the role of blood clotting formation. As such, consuming okra can help to rejuvenate both the skin and the hair.
You can read more on okra and its benefits in this post as well as on vitamin C and the skin in this post. How about a recipe? Try the okra punch by visiting this post.
7 ‘must know’ health benefits of Okra including its positive effects on the skin and blood
Oh, So Bright – Six (6) Skincare Benefits of Vitamin C and how to add it to your Skincare Regimen
Recipe – Okra Punch – It’s All About the Fiber!
Grapes and the Skin
Grapes (Vitis Vinifera) is a fruit that contains an abundant supply of polyphenols including anthocyanins (Costa et. al. 2014), resveratrol (Singh et. al., 2015) flavan-3-ols and proanthocyanidins (Unusan, 2020). These are powerful substances that act as antioxidants for the body and its overall health.
In a study of twelve (12) Japanese women with melasma (brown patches on the skin), it was found that supplementation of a grape seed extract supplement over six months significantly reduce the size of the melasma as well as lightened the skin (Yamakoshi et. al. 2004). It must be noted that for this study, the grape seed supplement consumed had 162 mg of proanthocyanidins (chemical compounds that give fruits, flowers and plants their red, blue or purple hue).
Another study by (Tsuchiya et al. 2020) with women between the ages of 30 to 60 years observed a significant reduction in lentigos (Liver spots) on the cheeks of these women after an 8-week consumption of 200 mg of dealcoholized red wine, which was high in oligomeric proanthocyanidins for 12 weeks. To obtain 162 to 200 mg of proanthocyanidins as stated in the studies, you would have to consume at least 300 to 382 mL or 1.3 to 1.6 cups of grape juice (Fam et. al. 2021).
One of the main compounds of grapes when it comes to skincare is ‘resveratrol.’ Resveratrol is considered a potent antioxidant, which is not only found in grapes (especially the red ones) but other foods such as berries, nuts, and red wine (Ren and Lien, 1997) and is purported to be able to form a defence for the skin which helps it combat harmful environmental stimuli (e.g., fungus or infection) (Renaud and Lorgeril, 1992). Resveratrol purportedly may help with fine lines and wrinkles, improving the elasticity of the skin, boost the firmness of the skin, improve hyperpigmentation (discolouration) as well as help with inflammation of the skin (Ratz-Łyko and Arct, 2018). As such, grapes have proven an excellent fruit to consume, not only for overall health but for beautiful skin.
To get these benefits, you can add more grapes to your diet or foods high in resveratrol. Additionally, you can get also try supplements in the form of grape seed extract or one with just resveratrol.
You can read more on these and other potent antioxidants that can help with the health of the skin in these posts:
Blueberries – They are more than just for Brain Health – Here are five (5) awesome benefits worth knowing!
Cranberries – The little red berries with some ‘Huge’ health benefits – Here are 5 worth knowing!
Pomegranates and the Skin
Pomegranate (Punica granatum) is a fruit that belongs to the Lythraceae family. Those little reddish, round-shaped things inside are called arils and these are usually eaten fresh or powdered (dried arils) (Encyclopedia Britannica). The juice of the pomegranate contains a substance known as ‘grenadine’ which makes the famous grenadine syrup, which is usually used for flavouring and liqueurs (Encyclopedia Britannica). While pomegranate is known for its many health benefits, it is also been associated with beautiful skin. As such, like grapes, pomegranates are rich in anthocyanins and ellagic acid (Kalaycıo and Erim, 2017). It also possesses a high amount of dietary fiber, folic acid, and vitamins C and K (Encyclopedia Britannica).
In a study with seventy-four (74) women between the ages of thirty (30) to forty (40), it was found that a daily intake of 8oz (237 mL) of pomegranate juice or its extract significantly impacted the minimal erythema dose (MED) of the patients (Henning et al., 2019). Additionally, this change was observed after 12 weeks. The minimal erythema dose is the Ultraviolet (UV) dose that is required to produce a minute amount of erythema 24 hours after UV exposure (Sekar and Srinivas, 2013). Erythema is defined as any abnormal redness of the skin that can be caused by some injury or inflammation among other conditions (Encyclopedia Britannica).
Additionally, research also found that pomegranate powder significantly reduced wrinkle formation and prevented the reduction of type 1 collagen and hyaluronan (Kang et al. 2017). It was also found to increase the water content of the skin in mice that were treated with Ultraviolet B rays (UVB) when compared with the group that did not consume the powder (Kang et al. 2017).
You can read more on some of these potent antioxidants that can help with the health of the skin in these posts:
Elderberry – What it is and Five (5) Benefits that make it one of the world’s renowned berries.
Quercetin – A Powerful Flavonoid and Immune System Defender
Nuts and Legumes and the Skin
These food kinds possess an abundant amount of fats (the good fats) and also serve as an excellent source of protein and vitamins. Research has shown that the high intake of polyunsaturated fatty acids, which comprises most nuts (e.g., Pistachios, peanuts etc.) can lower one’s risk of severe photoaging which is one of the signs of aging (Latreille et a., 2013). The study also purported that women with a high intake of n-3 PUFAs (Omega-3), especially eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) had a reduced risk of severe photoaging (Latreille et a., 2013).
Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) is a part of the omega- 3 fatty acid family. It can be found in fatty fish such as salmon. Along with the other famous docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), it can be found in fish oil supplements (Institute of Medicine, US, 2011). It is recommended that one consumed at least 5 oz of seeds and soy products weekly to experience skincare benefits (76). Nonetheless, for particular skin benefits, one may have to consume higher amounts.
You can read more on nuts and their benefits in this post
Cocoa and the Skin
Cocoa (Theobroma cacao) is the concentrated powder that makes chocolate liquor (a paste) that is derived from cocoa beans (Encyclopedia Britannica). As such, it is the key ingredient in chocolate. Cocoa is rich in flavonoids such as flavan-3-ols, which is said to be able to inhibit the peroxidation of lipid as well as neutralize and chelate metals that serve to enhance the creation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) (Scapagnini et al. 2014). It can also help the body manage stress thus serving as a protective agent for the body against it (100).
In a study among Korean women between the ages of 43 to 86 years, it was found that the daily consumption of a cocoa beverage of 320 mg of flavanols, significantly improve skin roughness and improved the depth of wrinkles (Yoon et al. 2016). It must be noted that this study was conducted over 24 weeks.
Additionally, the consumption of a cocoa beverage for even a shorter period (12 weeks) significantly caused a reduction in UV-induced Erythema as well as in skin roughness and scaling (Heinrich et. al. 2016). It also purportedly increases the density of the skin, and improved skin thickness, hydration as well as overall blood flow (Heinrich et. al. 2016).
Illustrative Summary
Here is an illustrative summary of the Five (5) Foods that can help with overall SKIN HEALTH!
Let’s Sum Up!
What we eat plays a great role in the overall look, and feel of the skin. While many foods possess nutrients that can benefit the skin, some have been proven by research to have potent substances for skin care. These include the foods mentioned in this post namely okra, pomegranate, grapes, etc. These foods have been shown to possibly help with minimizing or managing those pesky signs of aging, including hyperpigmentation, and smoothing of the skin among other excellent benefits for overall skin care.
So, while you peruse the beauty aisles for those topical products for your skincare journey, do not forget to visit those grocery aisles to stock up on these foods that have been proven to enhance the overall look and feel of the skin as well. Remember, true beauty starts from within.
Now, with all that was said… Are you Skintimate yet?
You can read more about foods and ingredients that can help you on your skincare journey:
Vitamin D and the Skin – Three (3) major benefits worth knowing!
Vitamin E and the Skin – Three (3) major benefits worth knowing!
Glycolic acid, the Sting of Beauty!
Benzoyl Peroxide Vs. Salicylic Acid for Acne – What are they and How can they help with Acne and General Skincare?
Aging like a Boss!
- What are sunscreens – Benefits and Ingredients to Look out for when Purchasing?
References
- Bakre, L. G., & Jaiyeoba, K. T. (2009). Effects of drying methods on the physicochemical and compressional characteristics of Okra powder and the release properties of its metronidazole tablet formulation. Archives of Pharmacal Research, 32 (2), 259-67.
- Britannica, T. Editors of Encyclopaedia (2022, June 9). erythema. Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/science/erythema
- Costa E, Cosme F, Jordão AM, Mendes-Faia A. Anthocyanin profile and antioxidant activity from 24 grape varieties cultivated in two Portuguese wine regions. OENO One. 2014;48(1):51-62. https://doi. org/10.20870/oeno-one.2014.48.1.1661
- Fam, Vivien & Charoenwoodhipong, Prae & Sivamani, Raja & Holt, Roberta & Keen, Carl & Hackman, Robert. (2021). Plant-Based Foods for Skin Health: A Narrative Review. Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics. 122. 10.1016/j.jand.2021.10.024.
- Gemede, H.F., Ratta, N., Haki, G.D., Woldegiorgis, A.Z., Beyene, F. (2015). Nutritional quality and health benefits of okra (Obelmoschus esculentus): A review. Pak J. Food Sci., 25(1), 16-25.
- Heinrich U, Neukam K, Tronnier H, Sies H, Stahl W. Long-term ingestion of high flavanol cocoa provides photoprotection against UV-induced erythema and improves skin condition in women. J Nutr. 2006;136(6):1565-1569. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/136.6.1565
- Henning SM, Yang J, Lee R-P, et al. Pomegranate juice and extract consumption increases the resistance to UVB-induced erythema and changes the skin microbiome in healthy women: A randomized controlled trial. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):14528. https://doi.org/10. 1038/s41598-019-50926-2
- Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Nutrition, Trauma, and the Brain; Erdman J, Oria M, Pillsbury L, editors. Nutrition and Traumatic Brain Injury: Improving Acute and Subacute Health Outcomes in Military Personnel. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 2011. 13, Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA) and Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA) Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK209320/
- Kalaycıo_glu Z, Erim FB. Total phenolic contents, antioxidant activities, and bioactive ingredients of juices from pomegranate cultivars worldwide. Food Chem. 2017;221:496-507. https://doi.org/10. 1016/j.foodchem.2016.10.084
- Kang S-J, Choi B-R, Kim S-H, et al. Beneficial effects of dried pomegranate juice concentrated powder on ultraviolet B-induced skin photoaging in hairless mice. Exp Ther Med. 2017;14(2):1023- 1036. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2017.4626
- Latreille J, Kesse-Guyot E, Malvy D, et al. Association between dietary intake of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and severity of skin photoaging in a middle-aged Caucasian population. J Dermatol Sci. 2013;72(3):233-239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdermsci.2013.07.006
- Lopez-Ojeda W, Pandey A, Alhajj M, et al. Anatomy, Skin (Integument) [Updated 2022 Oct 17]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441980/?report=classic.
- Ratz-Łyko A, Arct J. Resveratrol as an active ingredient for cosmetic and dermatological applications: a review. J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2019;21(2):84-90. doi: 10.1080/14764172.2018.1469767. Epub 2018 May 8. PMID: 29737899.
- Ren S, Lien EJ. Natural products and their derivatives as cancer chemopreventive agents. Prog Drug
- Res. 1997; 48:147–171. [PubMed: 9204686]
- Renaud S, Lorgeril Mde. Wine, alcohol, platelets, and the French paradox for coronary heart
- disease. Lancet. 1992; 339:1523–1526. [PubMed: 1351198]
- Scapagnini G, Davinelli S, Di Renzo L, et al. Cocoa bioactive compounds: Significance and potential for the maintenance of skin health. Nutrients. 2014;6(8):3202-3213. https://doi.org/10.3390/ nu6083202
- Schagen, Silke & Zampeli, Vasiliki & Makrantonaki, Eugenia & Zouboulis, Christos. (2012). Discovering the link between nutrition and skin aging. Dermato-endocrinology. 4. 298-307. 10.4161/derm.22876.
- Sekar C S, Srinivas CR. Minimal erythema dose to targeted phototherapy in vitiligo patients in Indian skin. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 2013;79:268
- Singh CK, Liu X, Ahmad N. Resveratrol, in its natural combination in whole grape, for health promotion and disease management. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2015;1348(1):150-160. https://doi.org/10.1111/nyas. 12798.
- Tsuchiya T, Fukui Y, Izumi R, Numano K, Zeida M. Effects of oligomeric proanthocyanidins (OPCs) of red wine to improve skin whitening and moisturizing in healthy women—a placebocontrolled randomized double-blind parallel group comparative study. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol. Sci. 2020;24:1571-1584.
- Unusan N. Proanthocyanidins in grape seeds: An updated review of their health benefits and potential uses in the food industry. J Funct Foods. 2020;67:103861. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2020.103861
- Yamakoshi J, Sano A, Tokutake S, et al. Oral intake of proanthocyanidin-rich extract from grape seeds improves chloasma. Phytother Res. 2004;18(11):895-899.
- Yoon H-S, Kim JR, Park GY, et al. Cocoa flavanol supplementation influences skin conditions of photo-aged women: A 24-week double-blind, randomized, controlled trial. J Nutr. 2016;146(1): 46-50. https://doi.org/10.3945/jn.115.217711https://doi.org/10. 1002/ptr.1537